5 Complications of Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes – In an earlier article, we talked about 5 signs that you could have type 2 diabetes, if you haven’t read that yet, then click the title to read that before enjoying this next article.
Today’s article is a follow up to that earlier one. If you ignore the signs of diabetes, or you fail to take your medications and allow diabetes to run uncontrolled, you will suffer major consequences. Diabetes is a systemic illness that has a negative effect on almost every organ in your body due to the persistently elevated blood sugar levels. In this article we look at 5 possible complications from poorly controlled diabetes.
1. Cardiovascular Complications
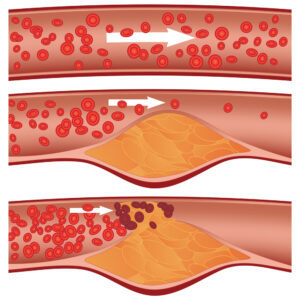
Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease, including coronary artery disease, heart attack, and stroke, due to atherosclerosis (hardening and narrowing of the arteries) . The High blood sugar levels cause damage blood vessels and speed up the development of atherosclerosis.
2. Kidney Disease (Nephropathy)
High blood sugar levels leads to kidney damage over time. This leads to diabetic nephropathy which can eventually progress to kidney failure, a condition that will require dialysis or transplantation.
3. Eye Complications
Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in working age adults, according to the US Center for Disease Control. Cataract and glaucoma are other eye conditions that can be caused by diabetes.
4. Nerve Damage (Neuropathy)
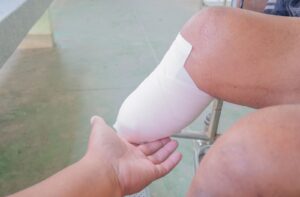
High blood sugar is toxic to peripheral nerves. These peripheral nerves carry sensation and positional signals to the brain and damage to these nerves will affect your ability to detect injuries to your body. It occurs throughout the body, but most severely in the lower limbs. A condition known as diabetic neuropathy. Symptoms can include numbness, tingling, pain, and muscle weakness. This is the single reason why diabetes remains the most common cause non traumatic amputations of the legs.
5. Reproductive and Sexual Health Issues
Diabetes can affect sexual function and fertility in both men and women. The combination of atherosclerosis and peripheral neuropathy could result in erectile dysfunction and impotence in men while high sugar levels can disrupt sperm production and cause hormone imbalance in both men and women resulting in difficulty in conception. Women who do achieve pregnancy in spite of diabetes or develop diabetes in pregnancy have a high chance of pregnancy complications and negative outcomes.
It’s important to note that the risk and severity of these complications can be reduced through effective diabetes management, including blood sugar control, a healthy diet, regular exercise, medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider, and routine medical check-ups. Early detection and intervention can also help prevent or mitigate many of these complications. It’s essential for individuals with diabetes to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a comprehensive management plan tailored to their specific needs.